Adenoids
What are adenoids?
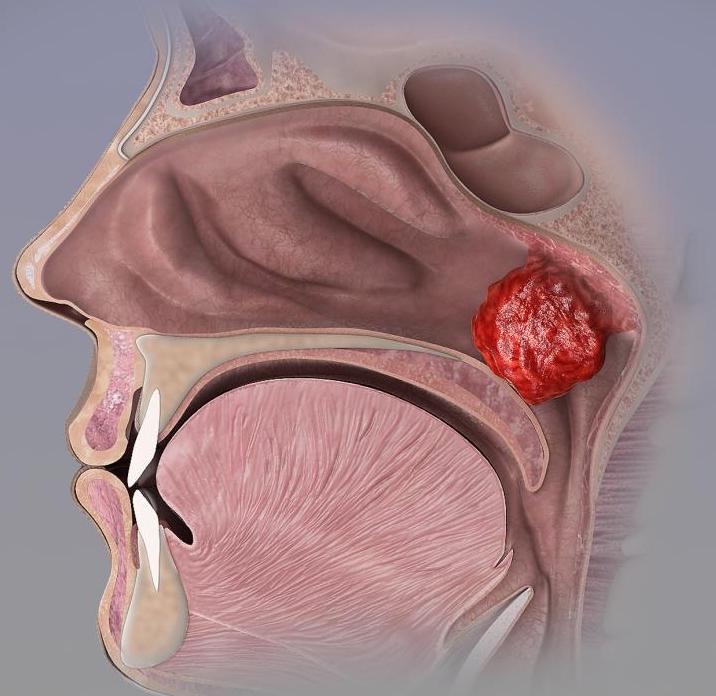
I am frequently asked this question. I am often guilty of assuming that most people know what adenoids are and what they do! Adenoids are located right at the back of the nose in the upper part of the throat. They are made up of “lymphoid tissue” which is soft in consistency. They are part of the immune system and help in the development of immunity. Together with the palatine and lingual tonsils, the adenoids make up Waldeyer’s ring of lymphoid tissue.
As I see and treat many international patients, I have had to learn the word for adenoids in different languages! Here’s a cheat list I use.
| Language | Term for Adenoids |
| Chinese | 腺样体 |
| Thai | โรคเนื้องอกในจมูก |
| Indonesian | Adenoide |
| French | Végétation adénoïde |
| German | Polypen |
| Italian | Adenoidi |
| Spanish | Adenoides |
Adenoids are large during the early years of life. Typically they are enlarged or hypertrophic between the ages of 3 and 8 years. We know that each infection starts in Waldeyer’s ring of lymphoid tissue and therefore causes a physiological enlargement. When infections are frequent, the adenoids may continue to remain enlargement and cause obstructive symptoms
How can enlarged adenoids be diagnosed?
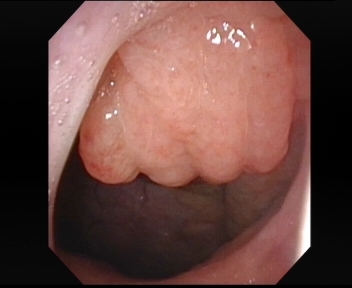
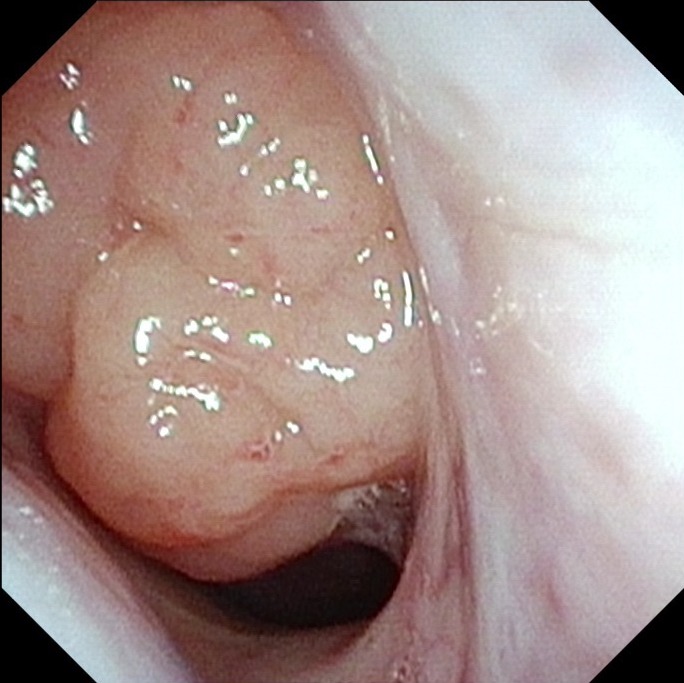
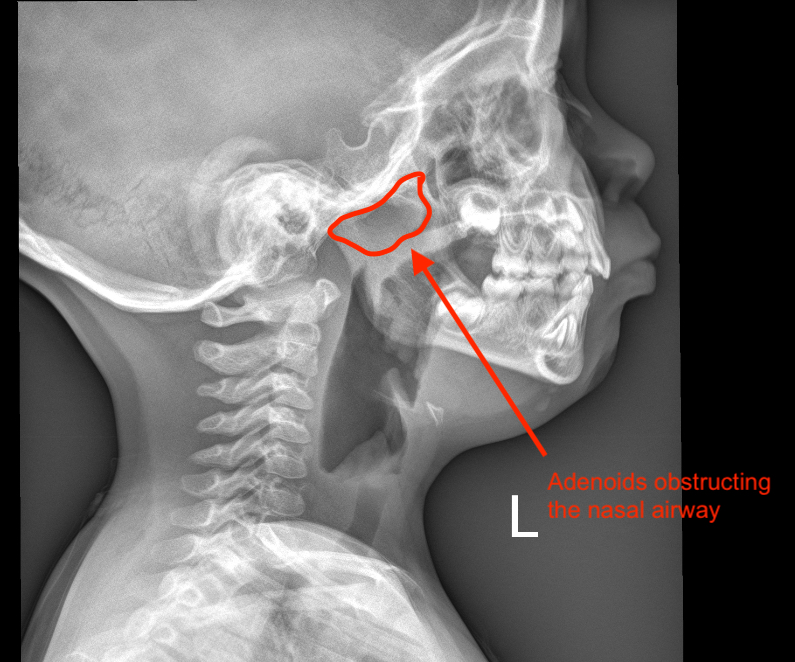
The simplest way to diagnose enlarged adenoids is to visualise the adenoids using nasal endoscopy. This is a relatively painless examination. The covid pandemic has made most patients less apprehensive of having things stuck into their noses! Yet in very young children I often ask for a simple postnasal space x-ray which gives adequate information about the size of the adenoids.
What problems do enlarged adenoids pose?
Enlarged adenoids pose the following problems
- Nasal obstruction that is persistent and worse when a child sleeps or has a cold
- Mouth breathing
- Dental and facial skeletal changes such as a receded lower jaw, a high arched palate, an elongated face (adenoid facies), and misalignment of the teeth (class II malocclusion)
- Sleep-disordered breathing or obstructive sleep apnoea
- Glue ear or thick fluid in the middle ear causing hearing loss and speech delay. This is sometimes known as otitis media with effusion (OME), serous otitis media, or chronic mucoid otitis media
- Recurrent respiratory tract infections
How can enlarged adenoids be treated?
Adenoid enlargement should be treated if they pose problems. It is important to stress that some enlargement is normal and given time will subside. Surgery is indicated for the persistently enlarged adenoids that lead to the problems mentioned above. Surgery to remove adenoids is called adenoidectomy. This is a common operation and you can read more about it here.
Share this blog via: